20 Oct · Science Explained
Unravelling the Mysteries of the Mind: How Does TMS Work?
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) harnesses electromagnetic induction to influence brain activity without surgery. Here is how this cutting-edge neuromodulation technique operates.
The Basics
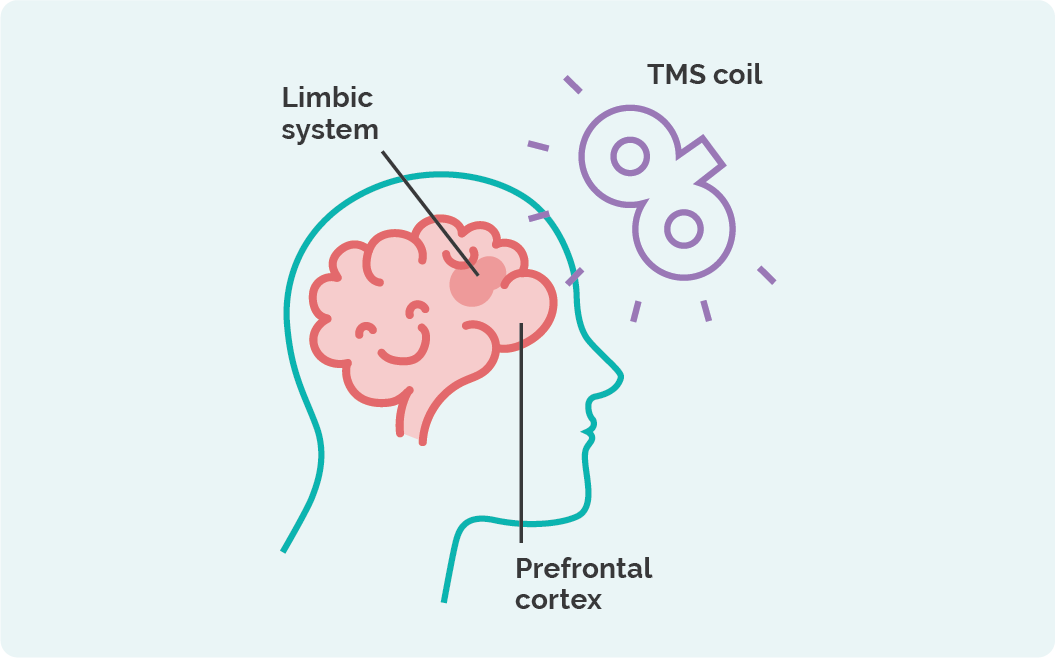
TMS devices include an electromagnetic coil placed near the scalp. When current flows through the coil, it generates a rapidly changing magnetic field that passes through the skull and reaches the brain without causing damage.
How Brain Activity Changes
The magnetic field induces electrical currents inside neurons, shifting charged particles and causing depolarisation (activation) or hyperpolarisation (inhibition). The outcome depends on stimulation intensity, frequency and duration.
Two Primary Modes
- Single-pulse TMS: Delivers individual pulses for mapping brain function, assessing excitability and studying cognitive processes.
- Repetitive TMS (rTMS): Sends trains of pulses to enhance or suppress neural activity, commonly used in clinical practice for depression.
Precision Targeting
TMS is highly specific. Clinicians adjust coil placement and orientation to focus on precise brain regions, making it possible to investigate or treat particular neural circuits.
As researchers continue to explore TMS, expectations are high that this technology will expand treatment options for neurological and psychiatric conditions.