20 Oct · Treatment Planning
The Benefits and Risks of TMS
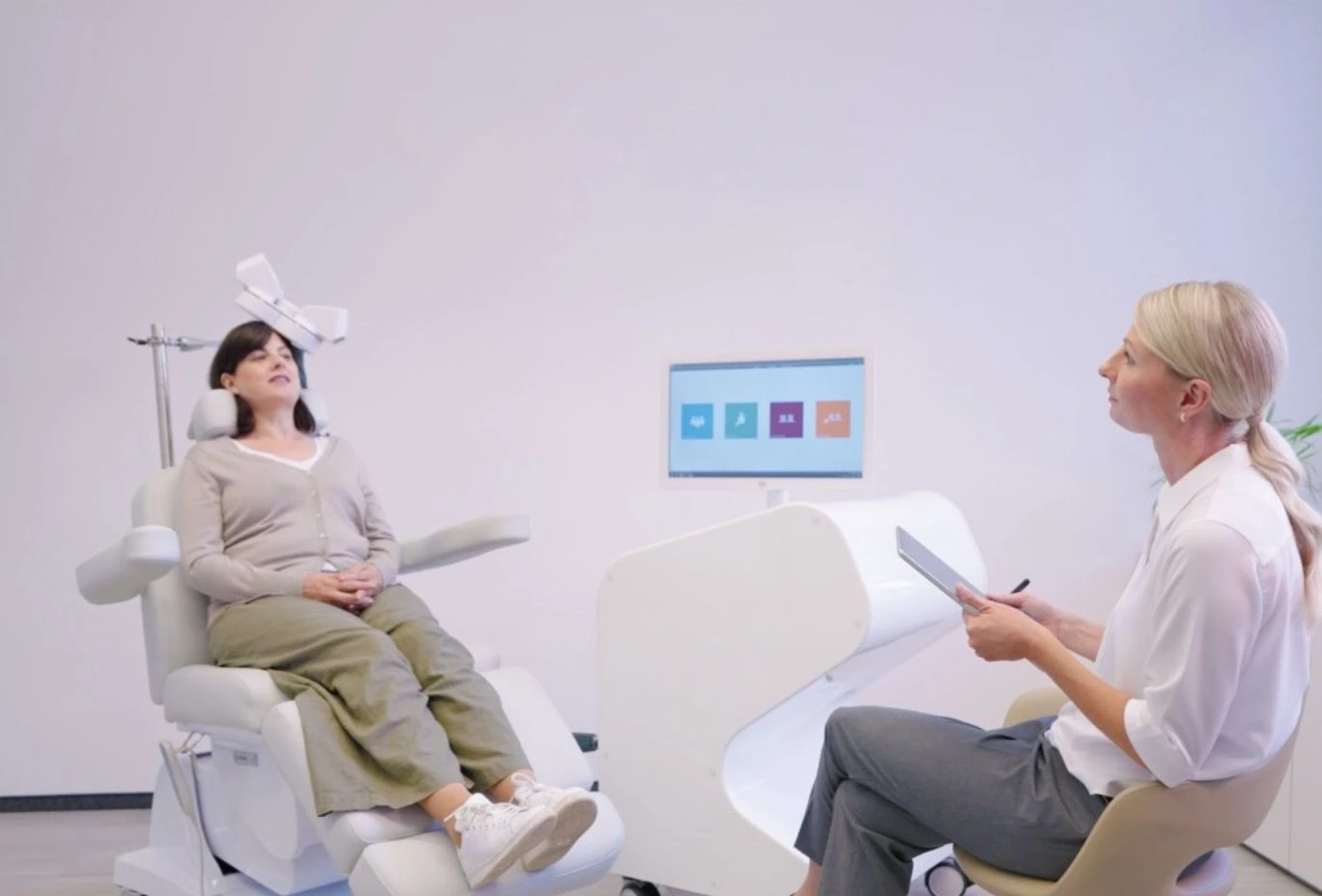
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) has emerged as a promising option for people who need non-invasive, targeted brain stimulation. Here is a balanced look at why many patients choose it—and what to consider before starting.
Benefits
- Non-invasive & painless: No surgery or anaesthesia is required, and sessions are well tolerated.
- Targeted stimulation: Clinicians can focus on precise brain regions to minimise systemic side effects.
- Efficacy for treatment-resistant depression: Many patients feel relief after other therapies have failed.
- Research utility: TMS helps scientists map neural networks and understand cognition.
- Potential for other conditions: Studies are exploring anxiety, OCD, PTSD, schizophrenia, chronic pain and more.
Risks and Considerations
- Side effects: Mild headaches, scalp discomfort or muscle twitches may appear but usually subside.
- Seizure risk: Very rare, and mitigated through careful screening and clinician oversight.
- Insurance access: Coverage varies by region; some private treatments incur out-of-pocket costs.
- Variable response: Outcomes differ person to person, so we monitor progress closely.
- Regulatory approvals: Indications depend on local authorities—always verify eligibility.
Before beginning TMS, consult with qualified healthcare professionals who can assess your medical history and determine whether the therapy suits your needs.